The Future of Cybersecurity: Tools and Strategies
The cyberthreat landscape is becoming increasingly complex and attackers are eager to take advantage of any digital vulnerability. How are decision makers using emergent strategies and tools to maintain effective cybersecurity?
One minute insights:
 Leaders are researching new cybersecurity solutions every week through online communities and peer conversations
Leaders are researching new cybersecurity solutions every week through online communities and peer conversations Emerging technologies like SOAR, CNAPPs and mobile MFA are seen as promising solutions in network, cloud, and IAM security respectively
Emerging technologies like SOAR, CNAPPs and mobile MFA are seen as promising solutions in network, cloud, and IAM security respectively Leaders are interested in new approaches to cybersecurity like zero trust and proactive security through AI
Leaders are interested in new approaches to cybersecurity like zero trust and proactive security through AI Most want to see more innovation in cloud and endpoint security
Most want to see more innovation in cloud and endpoint security Leaders expect attacks to become more sophisticated but are optimistic that cybersecurity will adapt
Leaders expect attacks to become more sophisticated but are optimistic that cybersecurity will adapt
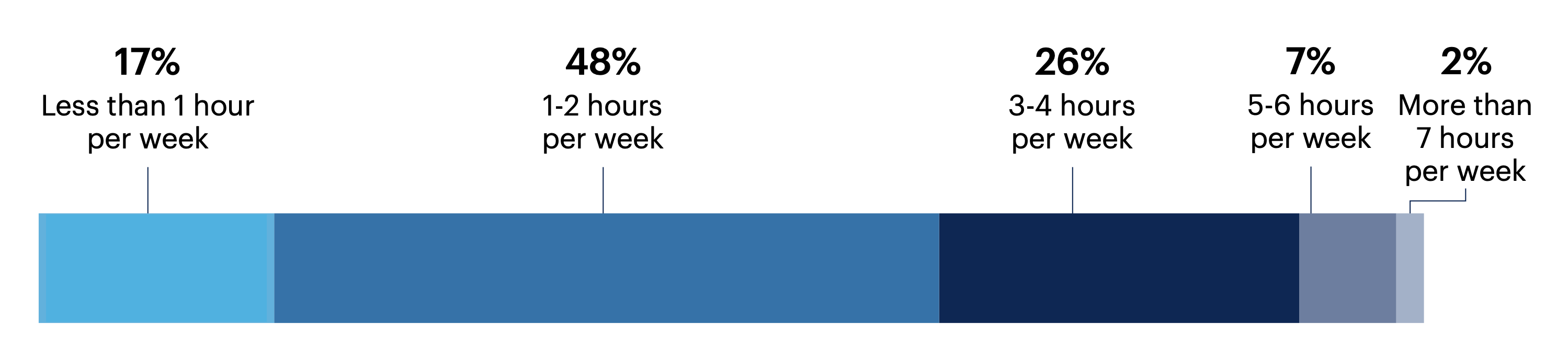
Most spend at least an hour a week researching emerging cybersecurity trends and technology, mainly through online communities and their peers
Most leaders (48%) spend 1-2 hours each week researching cybersecurity trends and emerging technologies. About a quarter (26%) spend 3-4 hours on this research each week.
How much time per week do you spend researching cybersecurity trends and emerging technologies?
n = 300
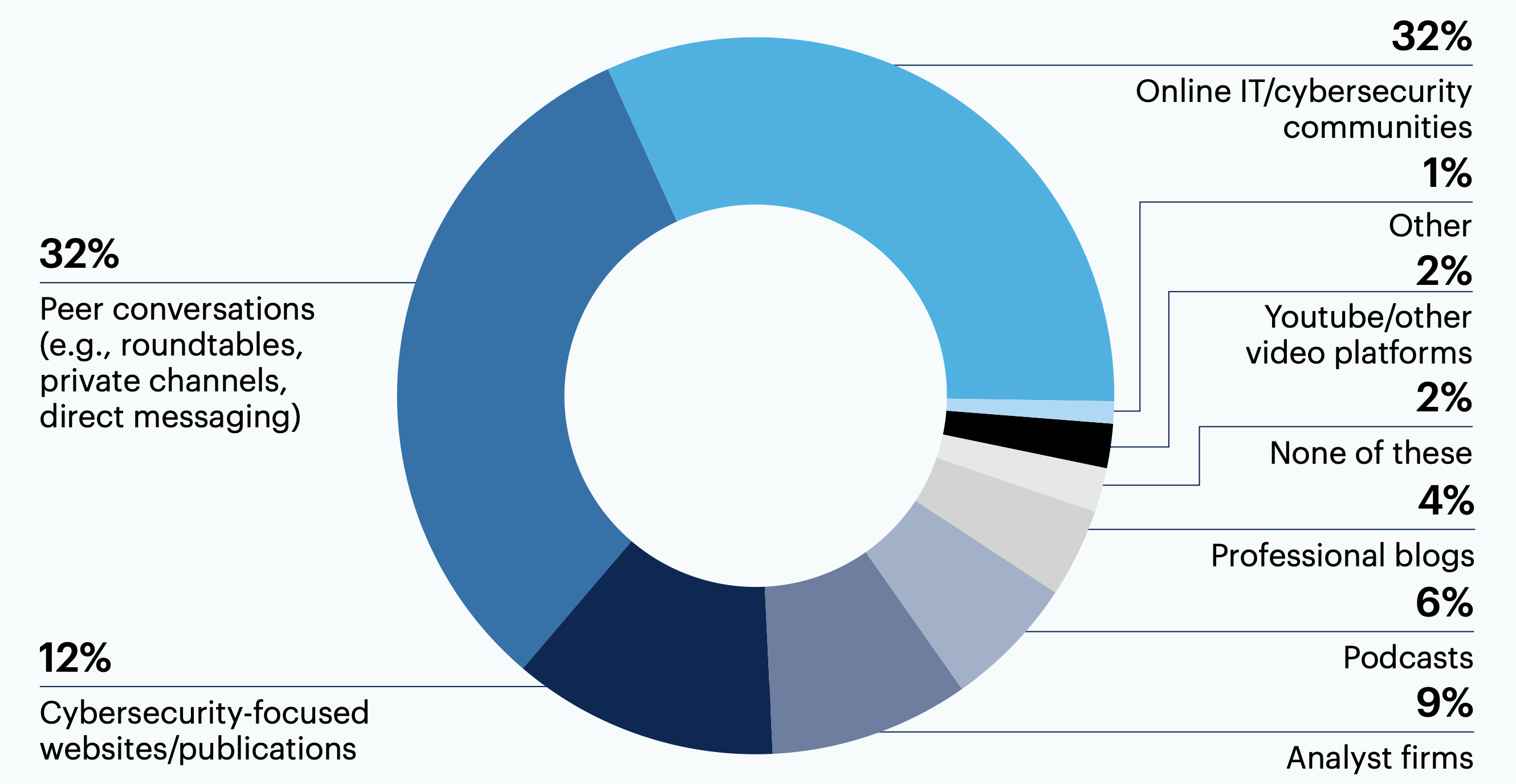
32% of respondents find online IT and cybersecurity communities the most valuable resource when conducting their research on cybersecurity trends and emerging technologies. Another 32% identified peer conversations as their most valuable resource.
What is your most valuable resource for researching cybersecurity trends and emerging technologies?
n = 300
[Cybersecurity] is getting more complicated.
Cybersecurity is essential for any organization to survive tomorrow.
Leaders are excited about a variety of emerging technologies in network security, cloud security and IAM
The top three emerging network security tools causing excitement among leaders include network access control (41%), secure access service edge (40%) and software-defined wide-area network (32%).
What emerging network security tools are you most excited about?
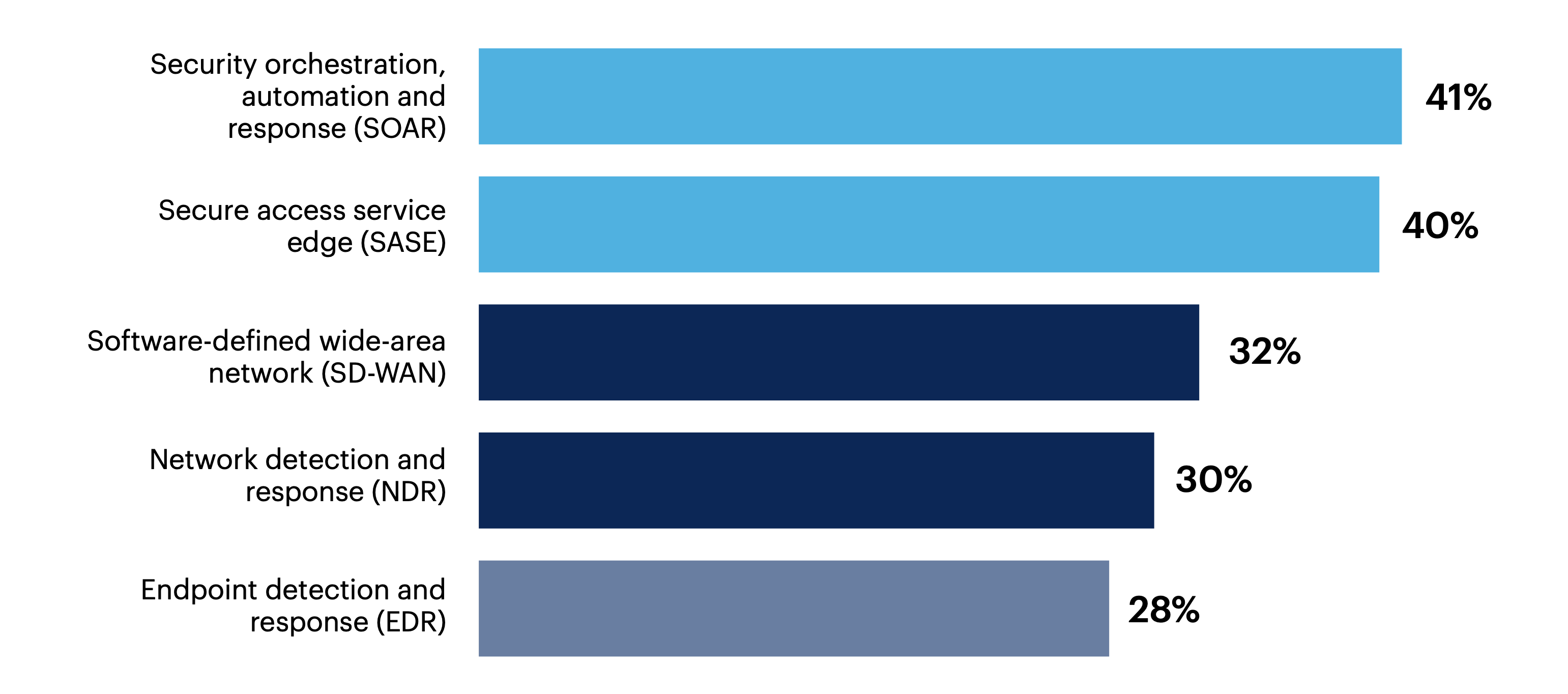
n = 300
User and entity behavior analytics (UEBA)24%, Intrusions prevention system (IPS) 23%, Network access control (NAC) 21%, Remote browser isolation (RBI) 19%, Zero trust network access (ZTNA) 19%, Extended detection and response (XDR) 15%, Desktop as a service (DaaS) 6%, None of these 2%, Other 1%
What emerging cloud security tools are you most excited about?
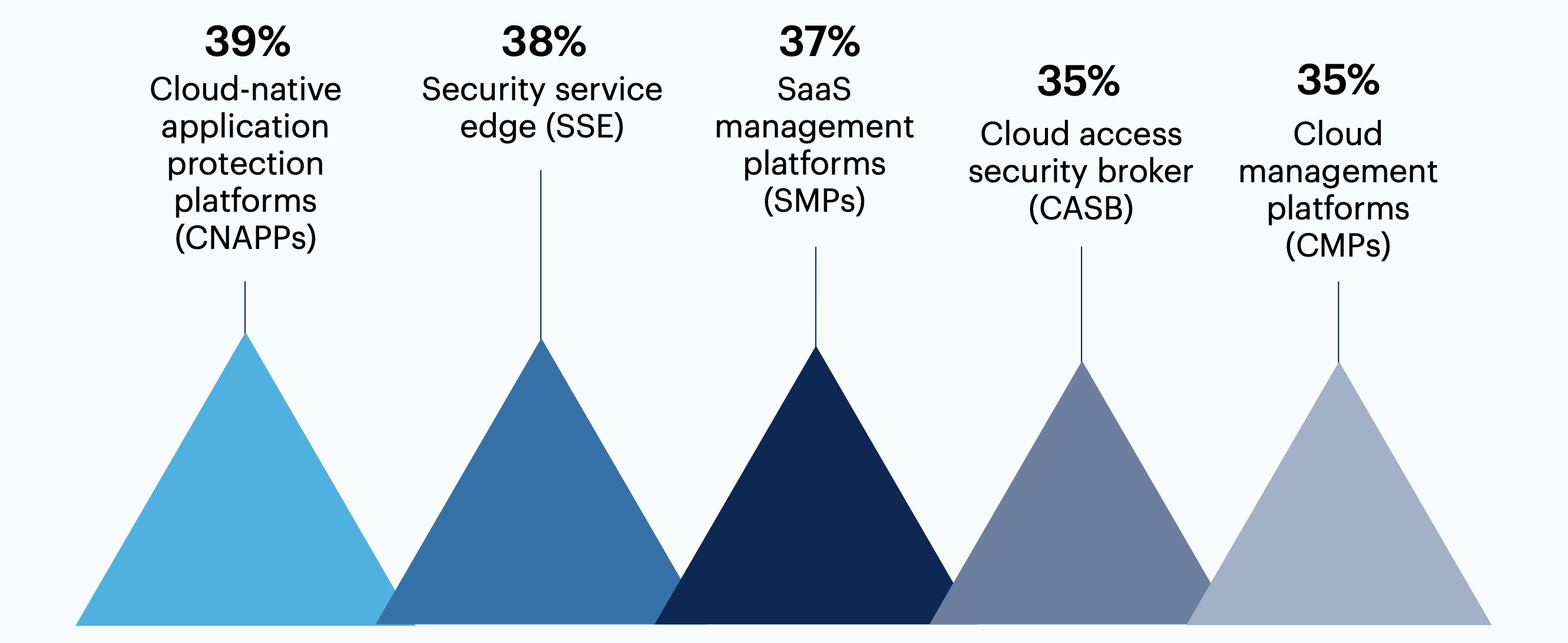
n = 300
Cloud data protection gateways (CDPGs) 31%, Cloud security posture management (CSPM) 24%, None of these 7%, Other 0%
Half of respondents (50%) identified mobile multifactor authentication as one of the emerging identity and access management tools they are most excited about. Many are also interested in biometric authentication (42%) and OAuth (39%).
What emerging identity and access management (IAM) tools are you most excited about?
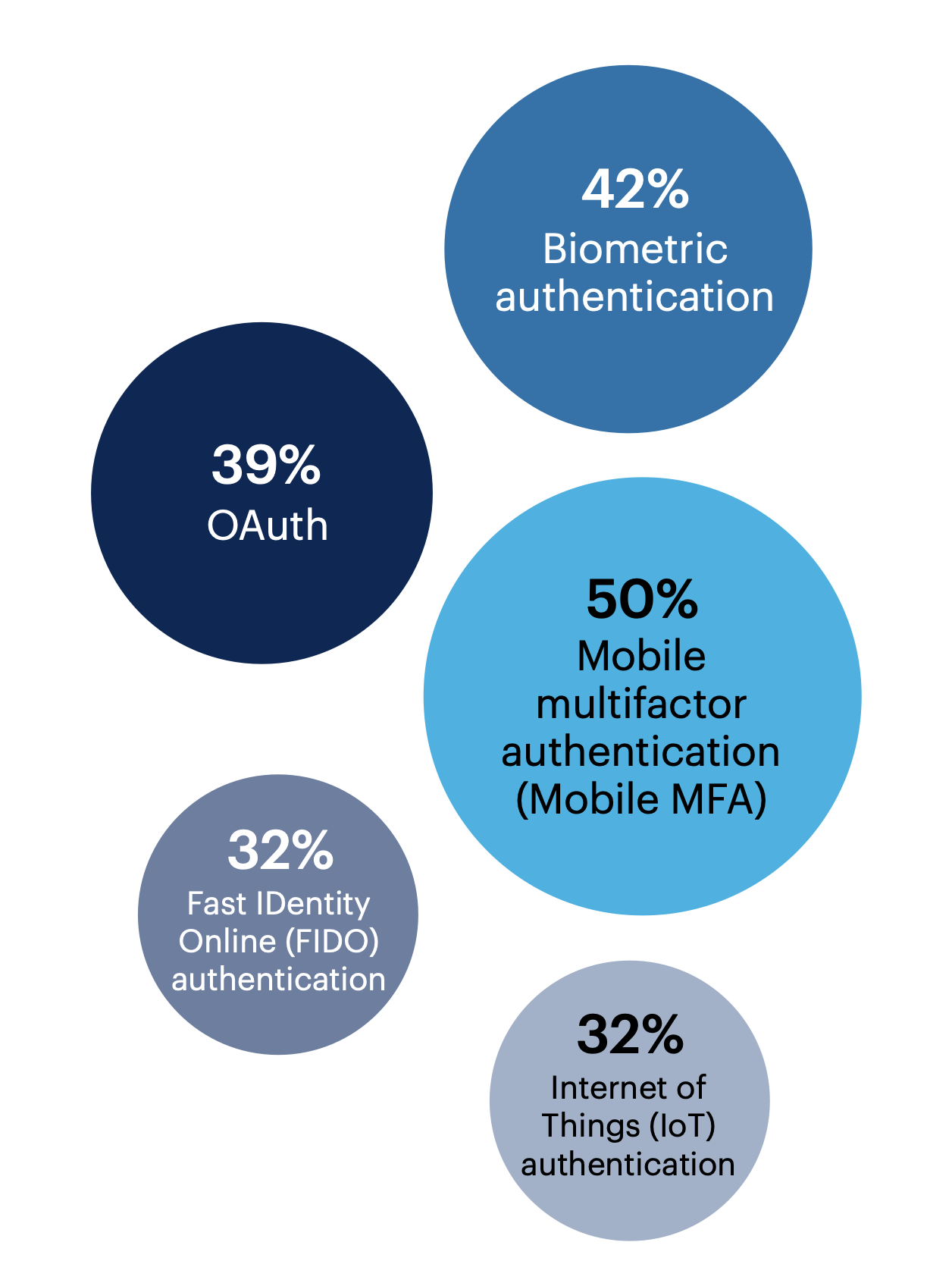
Decentralized identity 26%, Cloud infrastructure entitlement management (CIEM) 24%, Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) 14%, None of these 3%, Other 0%
n = 300
There are several interesting cybersecurity technologies I'm interested in.
[Cybersecurity is] moving from infancy to the awkward teenage years where we will see a lot of consolidation in the industry, fallout, and unexpected new solutions.
Emerging cybersecurity approaches like zero trust cause excitement, but cloud security and endpoint security need innovation
Which emerging approach to cybersecurity do you find most exciting?
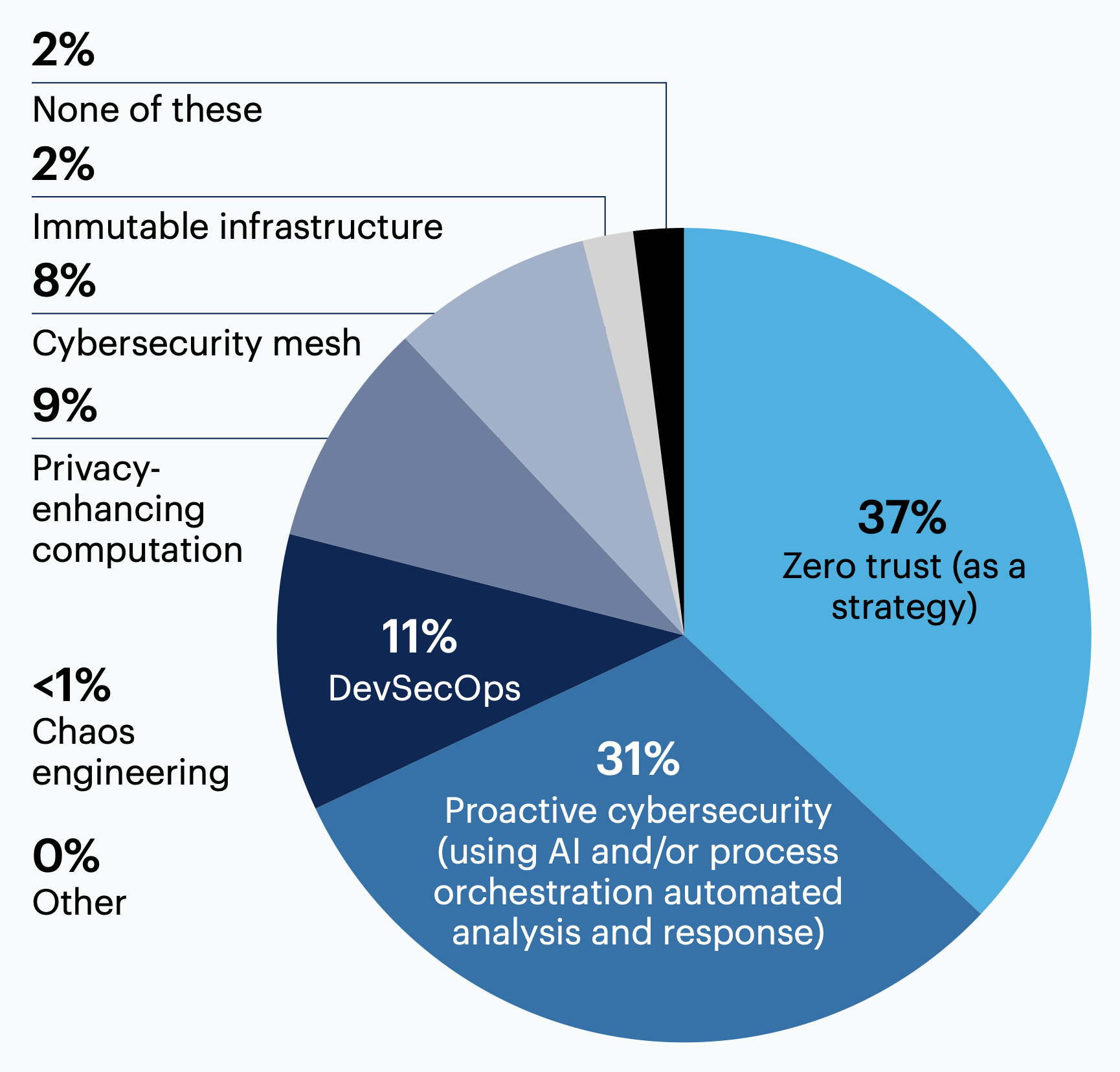
Leaders are most excited about emerging cybersecurity approaches like zero trust (37%) and proactive cybersecurity (31%).
n = 300
Which area of cybersecurity is most in need of innovation?
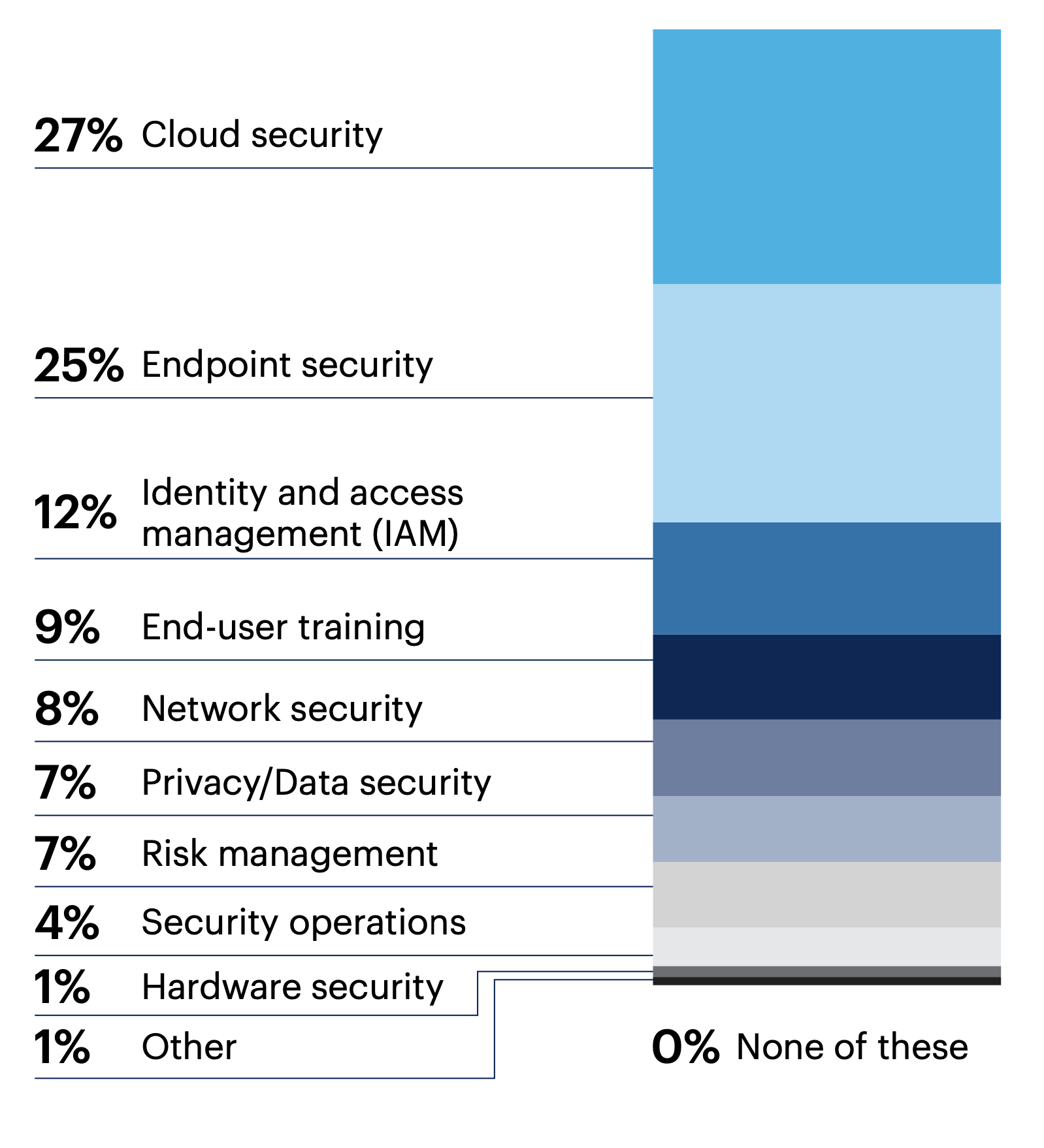
27% of respondents believe that cloud security is the area of cybersecurity in most need of innovation, while 25% point to endpoint security.
n = 300
Zero Trust Network Architecture is a game changer and needs to be implemented across all enterprises.
I believe AI and ML are important because users will continue to be the weakest link.
In the future, cybersecurity will need to contend with increasingly resourced and sophisticated attacks, but most feel optimistic about its adaptability
The top 3 identified challenges for the future of cybersecurity include attack sophistication (56%), greater resources for cyber attacks (44%) and hybrid work models (43%).
44% Greater resources for cyber attacks (e.g., state sponsorship) What are the top challenges for the future of cybersecurity?
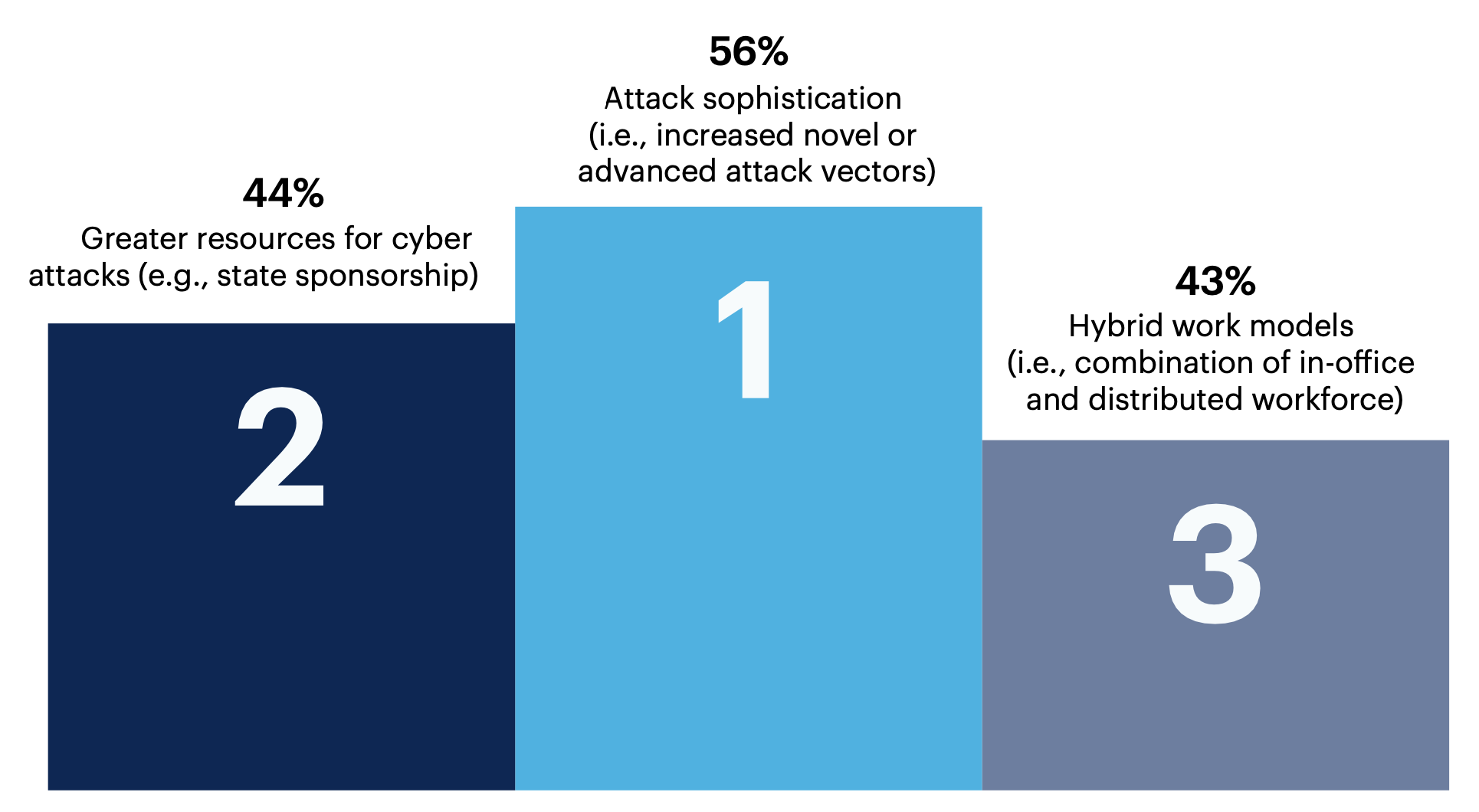
Blockchain technology (e.g., cryptocurrencies enabling anonymity/lack of traceability) 33%, Hiring (i.e., lack of qualified personnel) 29%, Increase in number of devices on the network (e.g., personal laptops, Internet of Things (IoT) devices) 17%, End-user security hygiene (e.g., poor password or data management) 15%, Talent management (e.g., skills development, talent retention) 15%, Cybersecurity framework limitations (i.e., frameworks out of date) 14%, Business support (i.e., cybersecurity still seen as an IT cost rather than a business continuity issue) 12%, Executive burnout (e.g., CISOs leaving the workforce due to stress) 10%, Lack of business skills in security leadership (e.g., inability to “sell” cybersecurity to the business) 9%, Punitive government measures (e.g., fines for cybersecurity breaches) 5%, None of these <1%, Other 0%
n = 300
Most leaders (71%) are optimistic that cybersecurity will be able to adapt and protect against future threats.
Do you feel optimistic or pessimistic about the ability of cybersecurity to adapt to and protect against future threats?
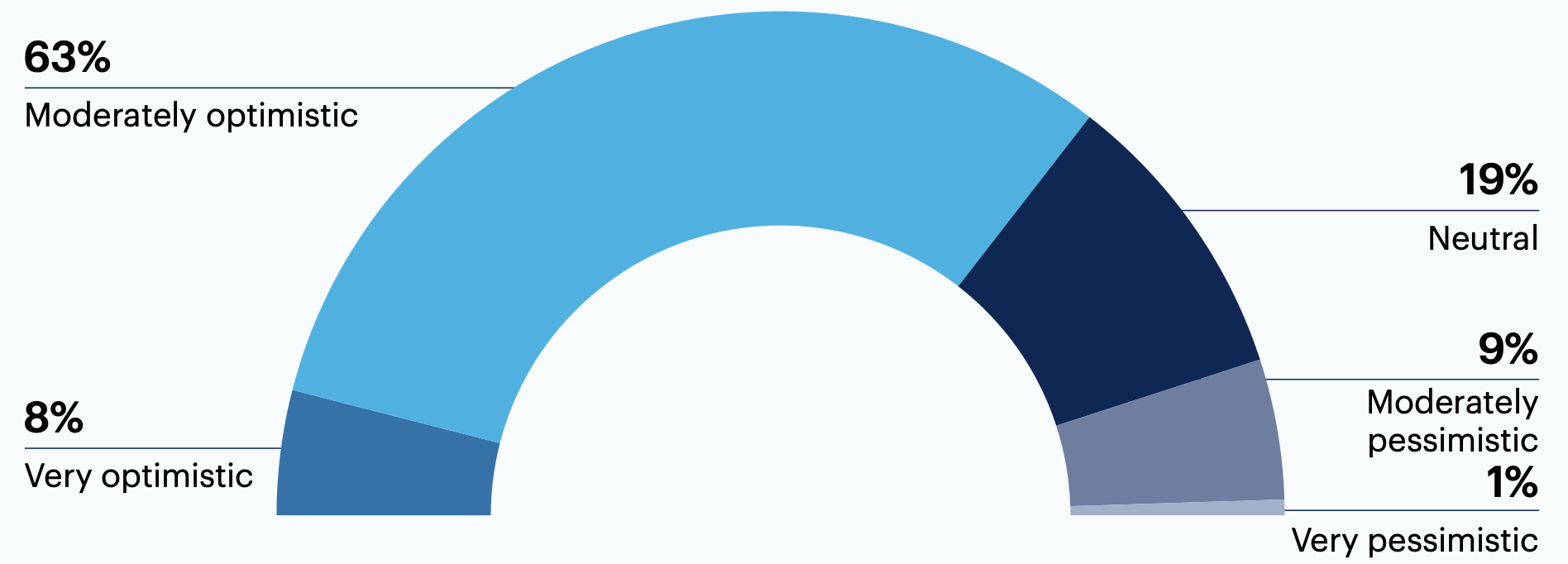
n = 300
[Cybersecurity] is going to be a challenge well into the future.
End-user cybersecurity training is still lacking but important as ever. I believe that there is an increase in attack reports due to ignorance and callous computing practices. Also, the law just has not been effective in indicting nation-state sponsors of attackers. The international governments and community have to do more to deter cyber-criminals.
The future of cybersecurity will be reliant on the training of future security analysts and the passing of information from our veterans.

Want more insights like this from leaders like yourself?
Click here to explore the revamped, retooled and reimagined Gartner Peer Community. You'll get access to synthesized insights and engaging discussions from a community of your peers.
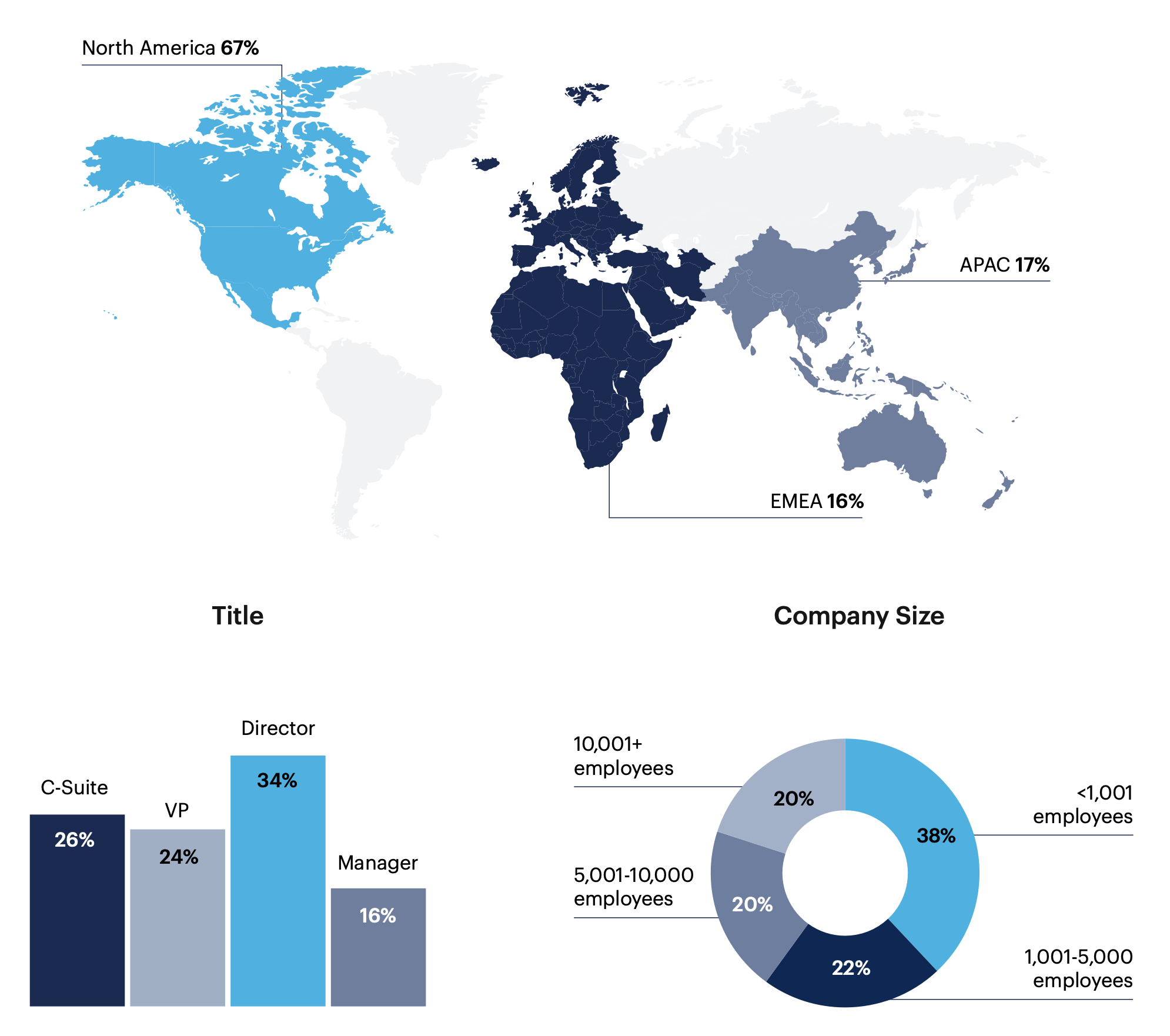
Respondent Breakdown
Region