IT and Infosec Collaboration on Vulnerability Patching
IT and infosec teams must work together to patch security vulnerabilities. How do organizations divide responsibility and support cross-functional collaboration?
One minute insights:
Majority of respondent organizations have a dedicated team for vulnerability patching
Leaders support eective IT-infosec collaboration with shared responsibilities matrixes and regular meetings
Most say having conflicting priorities between IT and infosec teams is one of the toughest vulnerability patching challenges
Majority of organizations use a dedicated team for vulnerability patching
The majority of respondents (51%) report that IT is primarily responsible for patching security vulnerabilities. At 29% of respondent organizations, the responsibility is equally shared between IT and infosec.
Which function is primarily responsible for vulnerability patching at your organization?

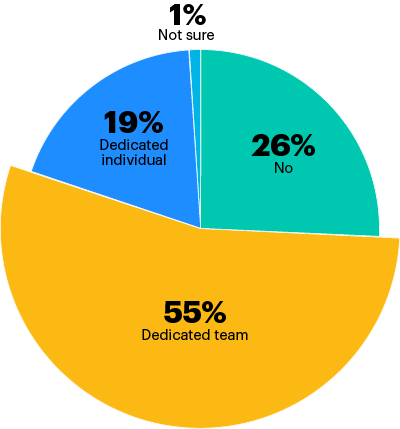
Nearly three-quarters (74%) of respondent organizations have one or more dedicated staff for patching vulnerabilities, with over half (55%) dedicating a team to this work.
Does your organization have any dedicated staff for vulnerability patching?
n = 187
Note: May not add up to 100% due to rounding
Question: Please share any final thoughts on vulnerability patching or IT-infosec collaboration at your organization. Feel free to elaborate on any planned improvements.
We’re moving the shared portion of [vulnerability patching] back to infosec.
We believe policy and governance for patching is best placed in infosec but IT [is] better placed to evaluate and execute. Risk and business continuity tradeos require collaboration.
Shared responsibilities matrix, regular meetings enable IT-infosec collaboration
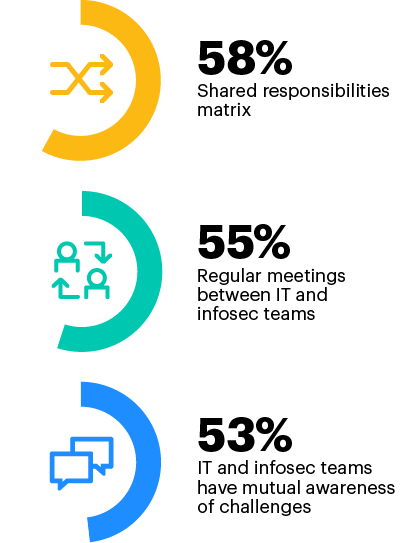
58% of surveyed leaders use a shared responsibilities matrix to support collaboration between IT and infosec teams charged with vulnerability patching. 55% rely on regular meetings.
How does your organization support effective collaboration between IT and infosec teams involved in vulnerability patching? Select all that apply.
Designated liaison(s) to coordinate infosec and IT teams 40% | Regular reporting across infosec and IT teams 36% | Clear handoff processes 34% | Centralized communication hub 32% | Documentation 32% | Defined communication plans 27% | Shared dashboards 24% | Regular training sessions 15% | Performance review criteria tied to remediation metrics 14% | Other* 1% | Not sure 0%
n = 187 *Other includes: One in the same
Question: Please share any final thoughts on vulnerability patching or IT-infosec collaboration at your organization. Feel free to elaborate on any planned improvements.
Must tie metrics and incentives to performance while respecting security’s role [in] enabling [a] secure business.
Good communication and shared goals are key.
Conflicting priorities between IT and infosec is a major challenge for patching
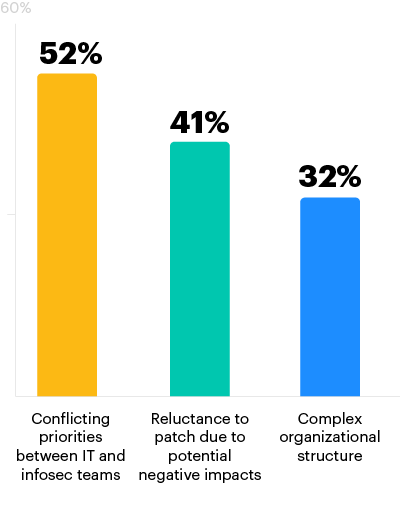
Over half (52%) of respondents say conflicting priorities between infosec and IT teams is one of their organization’s most difficult challenges with vulnerability patching.
41% cite the reluctance to apply patches for fear of negative outcomes among their most diicult hurdles.
What are the most diicult challenges your organization is facing in terms of collaboration between IT and infosec teams involved in vulnerability patching? Select up to 3.
Inconsistent handoff processes between teams 26% | Inadequate documentation 24% | Inadequate communication 21% | Insufficient training on security protocols for IT team(s) 21% | Unclear division of responsibilities 16% | Inadequate reporting 12% | Other* 3% | Not sure 2%
n = 187 *Other includes: Unsupported applications; We are fortunate to have a highly collaborative team between IT & [infosec]; Complexity of system downtime on critical apps and servers; Staffing on infosec teams, although it has improved; Other
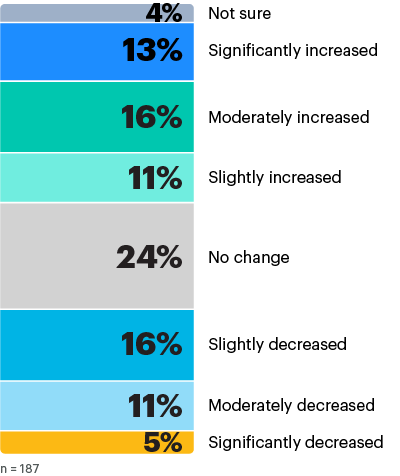
32% say mean time to remediation (MTTR) has improved over the past 12 months, noting decreases in MTTR for actively exploited vulnerabilities. But 40% say their organization’s MTTR worsened during this period.
Has the mean time to remediation (MTTR) for actively exploited vulnerabilities at your organization changed over the past 12 months?
Question: Please share any final thoughts on vulnerability patching or IT-infosec collaboration at your organization. Feel free to elaborate on any planned improvements.
Collaboration has improved but the rate of removal on unsupported applications where no patching is possible has slowed due to budget cuts.
Business downtime continues to be our biggest challenge when trying to negotiate windows to apply security patches.
In their own words...
Question: Please share any final thoughts on vulnerability patching or IT-infosec collaboration at your organization. Feel free to elaborate on any planned improvements.
We have significantly benefited by aligning cyclic OS patching with [the] rest of the vulnerability remediation and tool-based automation.
Patching for the sake of it doesn’t bring much value to the organization.
One key factor is having properly laid processes and monitoring for timely patching. We are also evaluating zero trust architectures/tools to make infra more secure and rugged.
Automating much of the patching has improved the situation for us. While there are situations where patches cause issues, we have preferred to deal with those situations rather than risk not keeping up with the security patching.
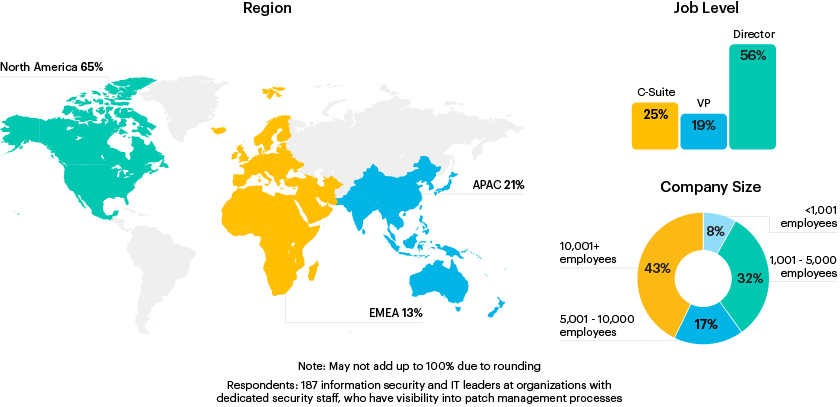
Respondent Breakdown